Mybatis-Plus的查询源码分析
前言
Mybatis-Plus为简化开发而生,本篇会根据BaseMapper的list方法一起看下其是如何实现查询的。建议先阅读上一篇,描述了BaseMapper是被动态代理类MybatisMapperProxy实例化,具体如何通过MybatisMapperProxy切入实现查询的本篇来揭晓。
示例
// model
@Data
@TableName("user")
public class User {
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
private String telPhone;
@TableLogic
private int deleted;
}
// mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {}
// serviceImpl
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService {}
// config
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL));
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
}
@Bean
public MybatisPlusPropertiesCustomizer mybatisPlusPropertiesCustomizer() {
return properties -> {
GlobalConfig globalConfig = properties.getGlobalConfig();
globalConfig.setBanner(false);
MybatisConfiguration configuration = new MybatisConfiguration();
configuration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(MybatisEnumTypeHandler.class);
properties.setConfiguration(configuration);
};
}
@Bean
public Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer customizer(){
return builder -> builder.featuresToEnable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_ENUMS_USING_TO_STRING);
}
}
单元测试类:
@Test
public void testSelect() {
List<User> userList = userService.list(new QueryWrapper<>());
System.out.println(userList);
}
源码分析
从测试类执行
1、首先会调用到IService的默认list查询方法
// com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService
default List<T> list(Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) {
return getBaseMapper().selectList(queryWrapper);
}
其中getBaseMapper方法由IService实现类ServiceImpl<M extends BaseMapper< T>, T>完成
// com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl
@Autowired
protected M baseMapper;
@Override
public M getBaseMapper() {
return baseMapper;
}
返回的就是MybatisMapperProxy实例,我们知道MybatisMapperProxy是一个代理类,代理BaseMapper的实现接口的,即示例中的UserMapper。
据JDK动态代理,在调用代理对象方法时,会进入代理类的代理行为方法invoke。
2、进入代理类MybatisMapperProxy的invoke方法
// com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.override.MybatisMapperProxy
// implements InvocationHandler
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 方法所在类不是Object的时候
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
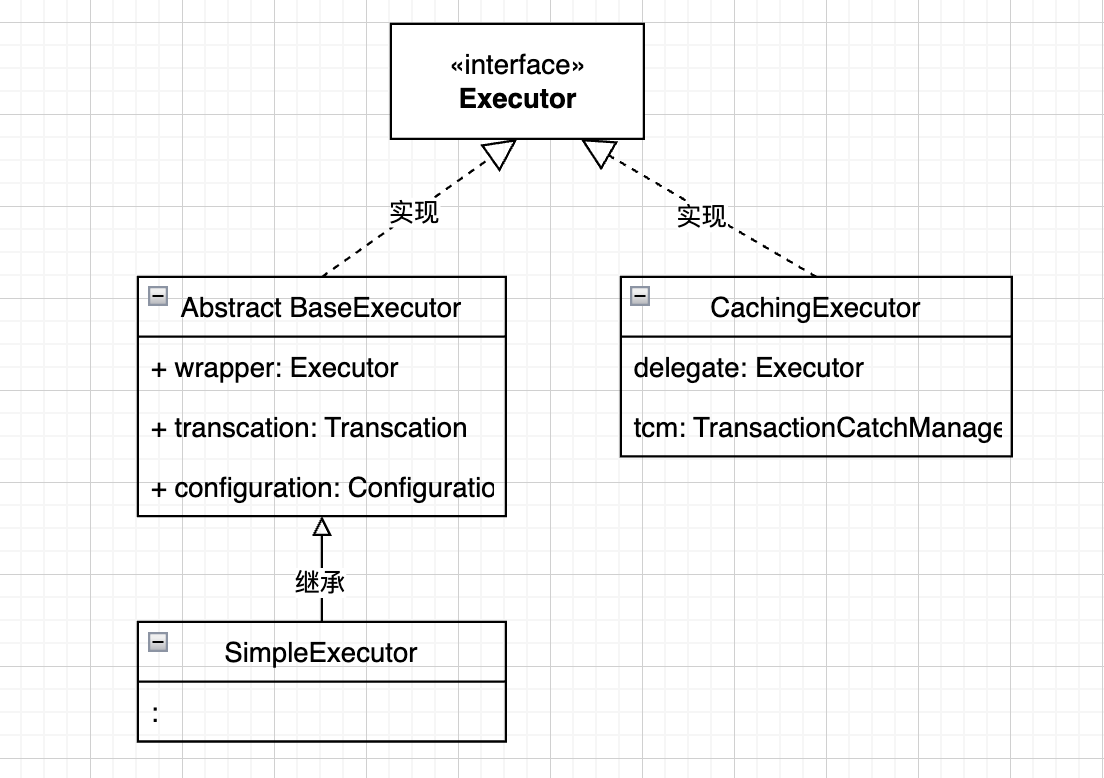
该类copy至org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy,主要区别在于其内部类PlainMethodInvoker使用的是MP的MybatisMapperMethod类
3、cachedInvoker(method)创建MapperMethodInvoker的实现类,进行后续的查询
3.1、进入当前类的cachedInvoker的方法
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
//// methodCache是一个Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker>缓存方法对应的Mapper的方法查询代理
return CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
//// 方法是默认方式时,接口的默认方法
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
//// selectList不是BaseMapper的默认方法,进入这里,创建PlainMethodInvoker,并使用MybatisMapperMethod作为参数
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MybatisMapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
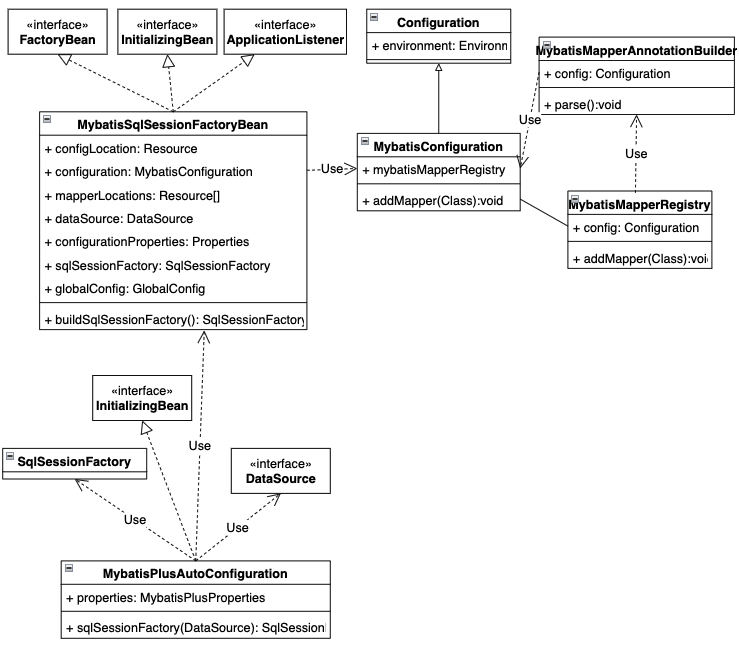
3.2、看下new MybatisMapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration())
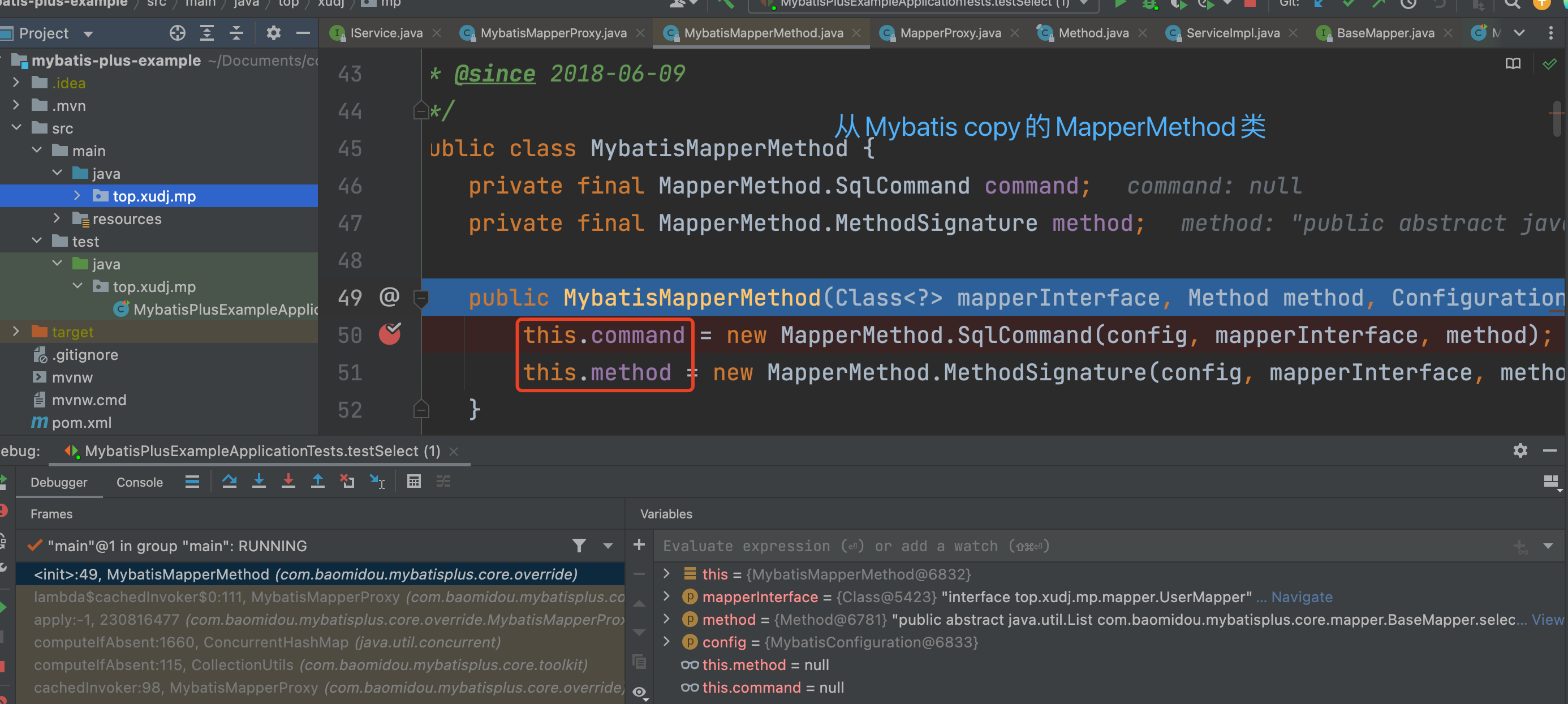
使用的MapperMethod.SqlCommand command与MapperMethod.MethodSignature method两个成员变量仍是Mybatis的MapperMethod的静态内部类,辅助后面的查询判断。
主要完成:
1)、定义查询类型和对应mappedStatement
this.command = new MapperMethod.SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
2)、查询方法的返回类型、是否返回多个,参数类型,@Param解析等
this.method = new MapperMethod.MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
MybatisMapperMethod{@link MapperMethod} copy 过来,主要添加了分页查询的场景。
3.3、创建完成MybatisMapperMethod对象,回到第3.1步,完成new PlainMethodInvoker创建,并添加到methodCache中。
4、执行PlainMethodInvoker的invoker方法,通过MybatisMapperMethod进行execute查询,如下图所示:
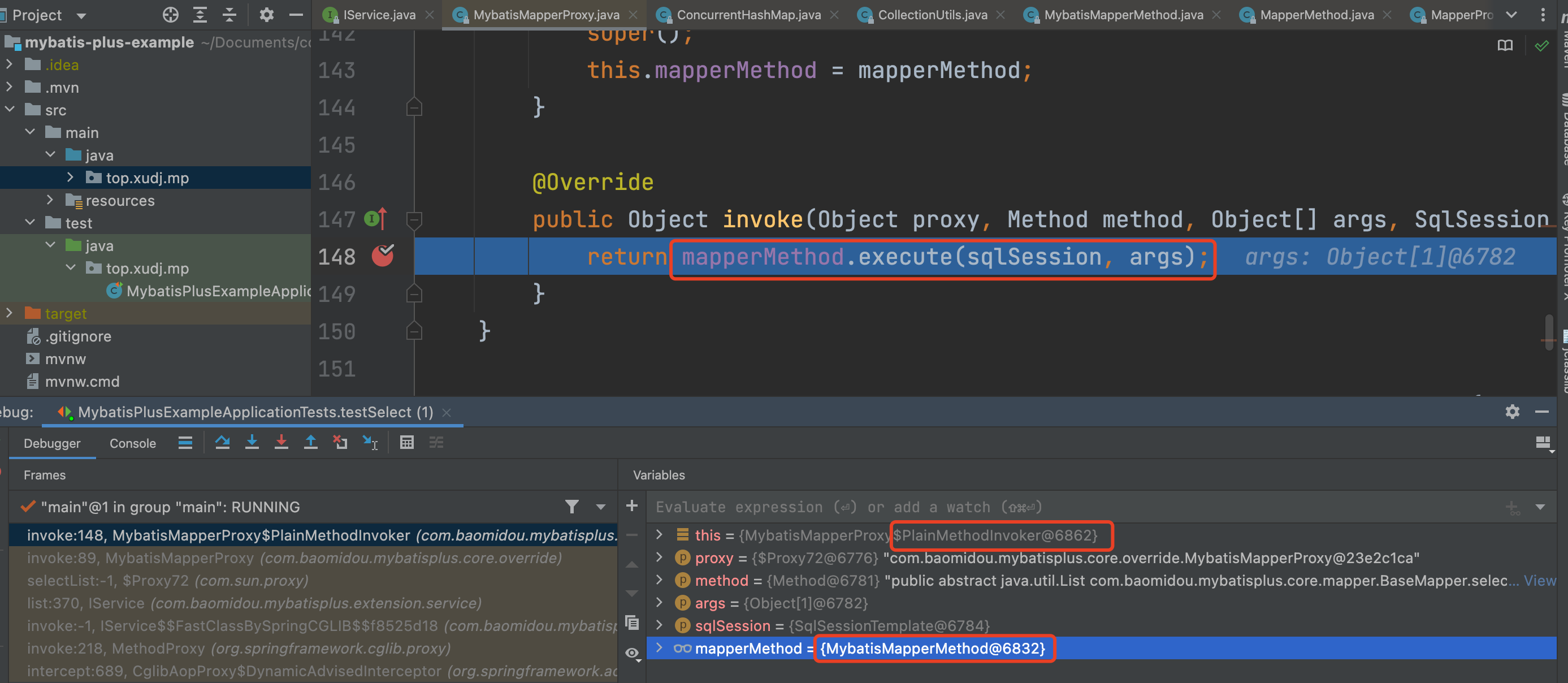
5、进入到MybatisMapperMethod#execute方法,根据方法返回类型等进行更细分的查询方法。
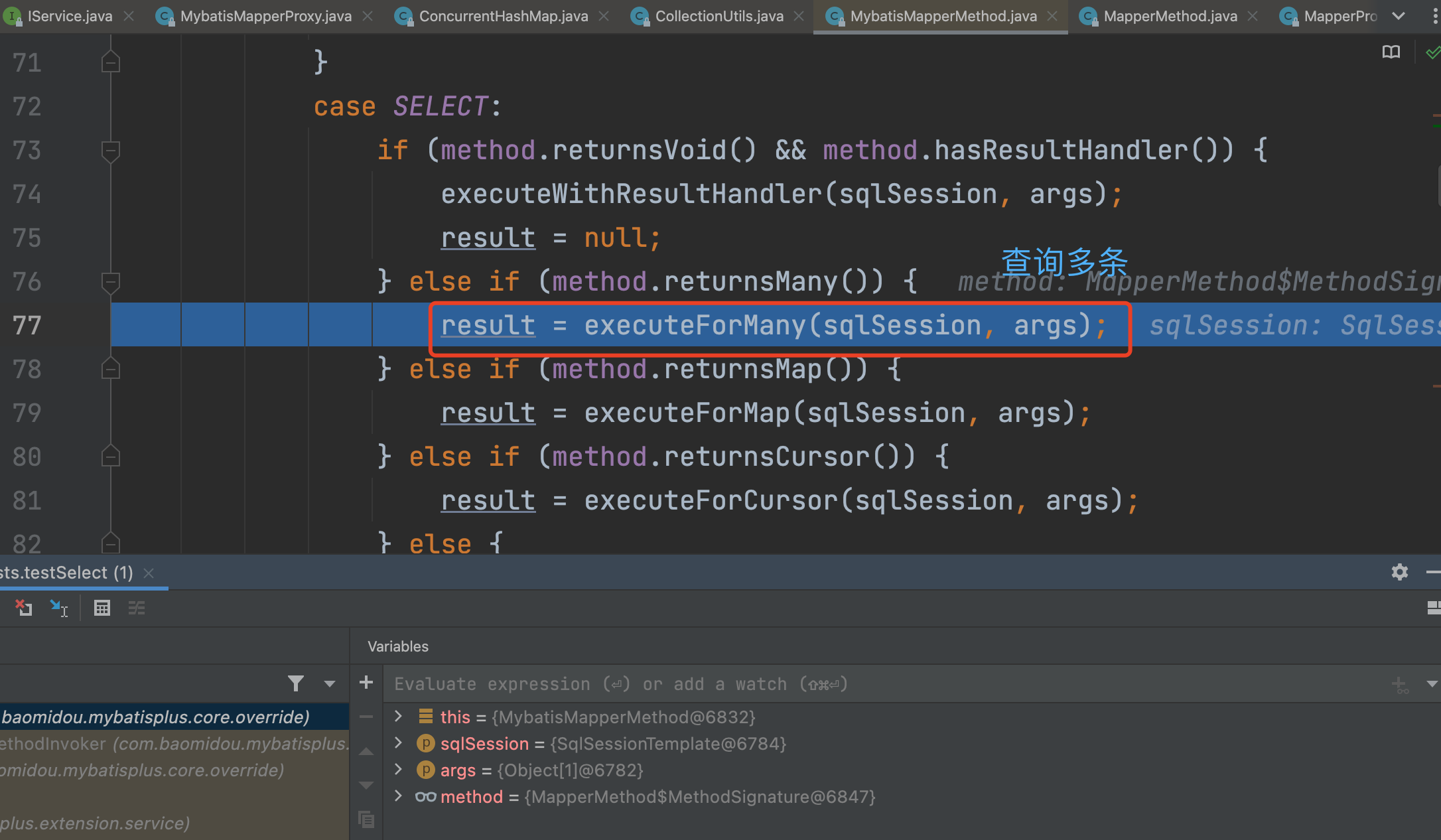
注意这里的sqlSession是在项目启动时注入到MybatisMapperProxy中的SqlSessionTemplate。
6、接下来就是通过sqlSession进行查询
这里的sqlSession是SqlSessionTemplate(Mybatis包中)
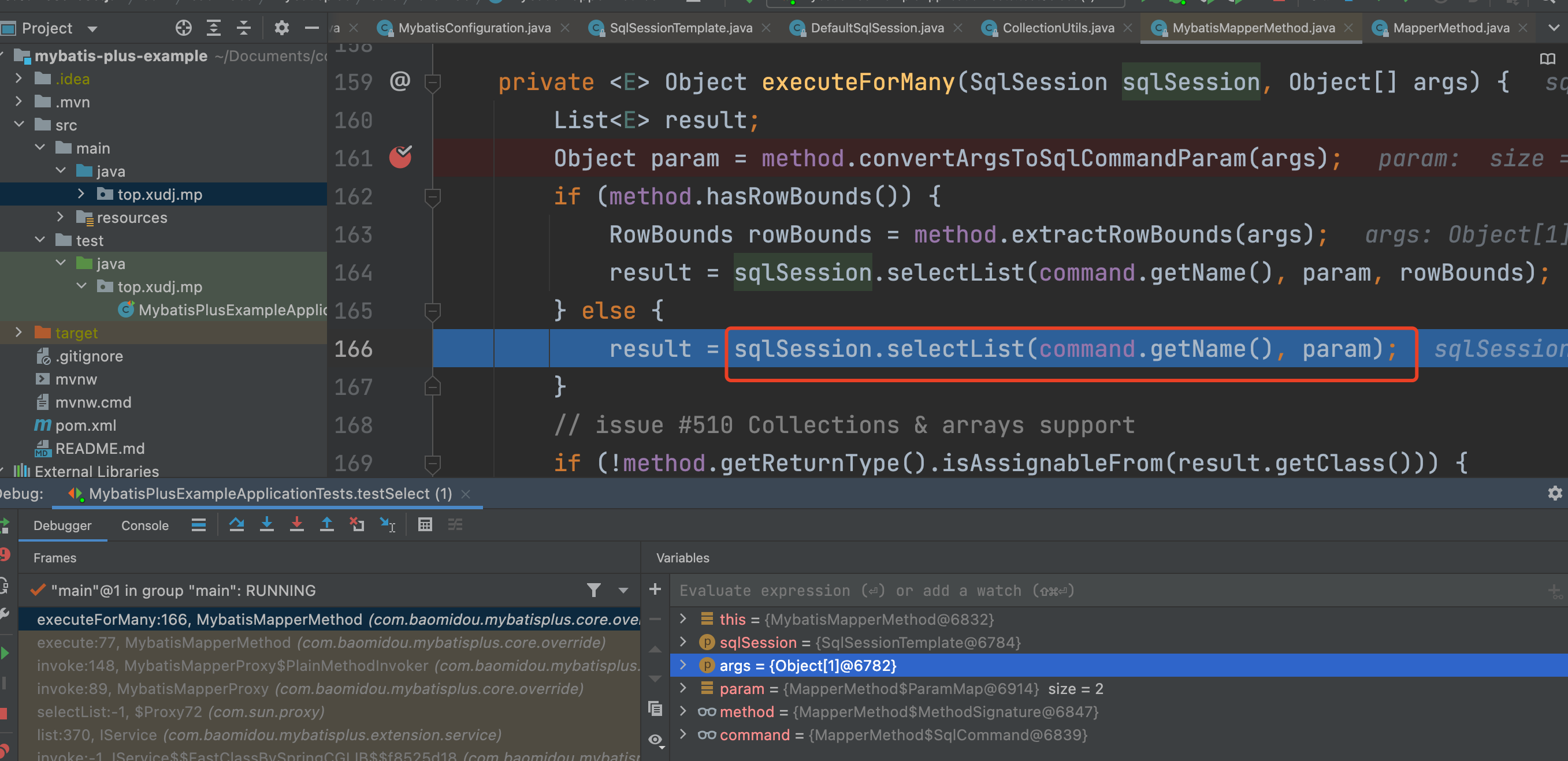
7、进入SqlSessionTemplate的selectList方法
// org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate
// implements SqlSession
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy.selectList(statement, parameter);
}
sqlSessionProxy是MyBatis中SqlSession接口的一个代理对象,用到了动态代理:
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class }, new SqlSessionInterceptor());
代理类是SqlSessionInterceptor,代理了SqlSession接口。
SqlSessionInterceptor是SqlSessionTemplate的一个私有内部类。
8、so,接下来的请求会进入到SqlSessionInterceptor的invoke方法:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//// 关键点,获取SqlSession对象,通过反射调用对应的method,即selectList方法
//// 看getSession方法
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
//// 执行对应方法
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
// force commit even on non-dirty sessions because some databases require
// a commit/rollback before calling close()
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
//// 省略部分
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
getSqlSession方法是import SqlSessionUtil的静态方法:
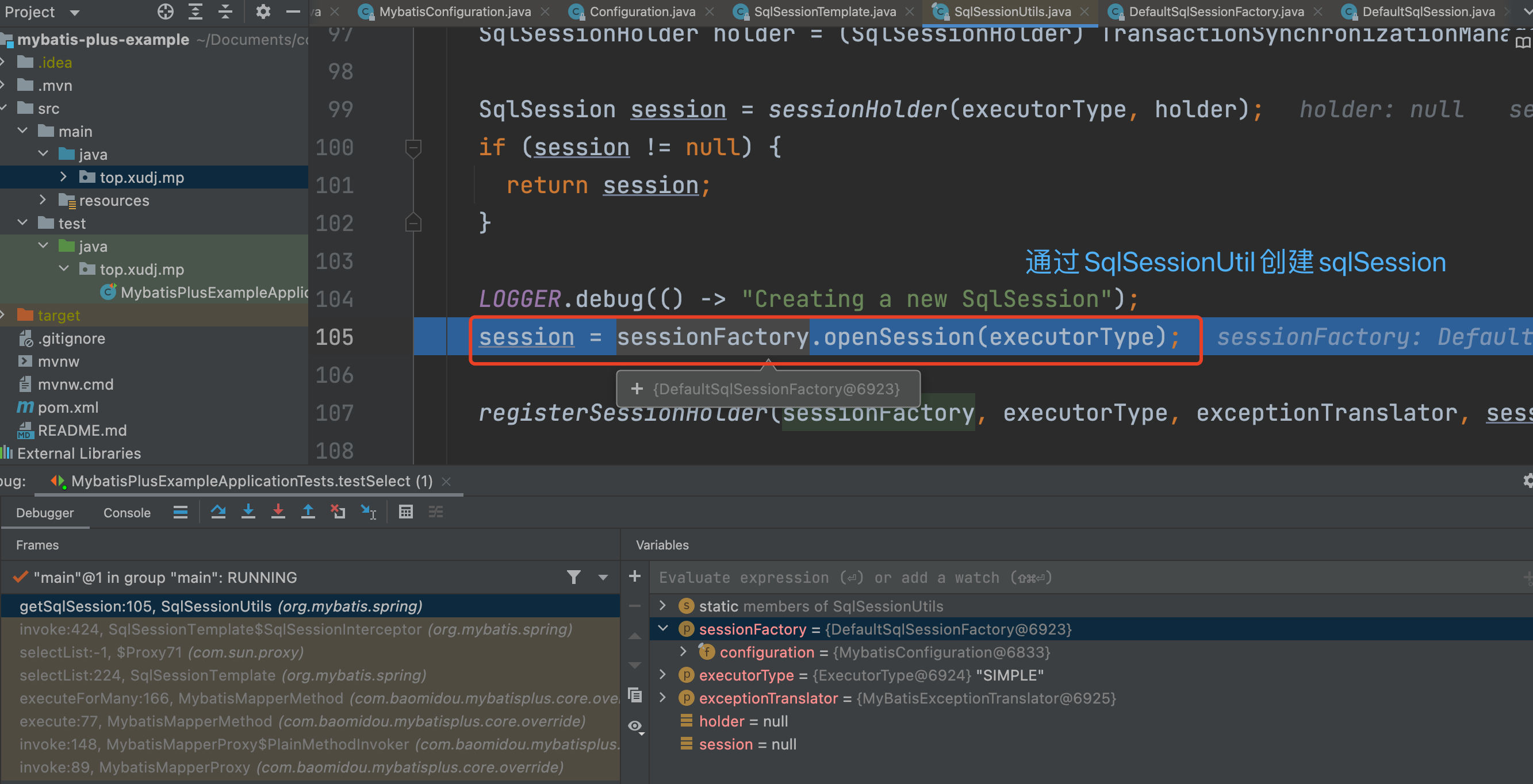
继续进入openSession方法,创建DefaultSqlSession。另有执行器Executor,事务Transcation等:
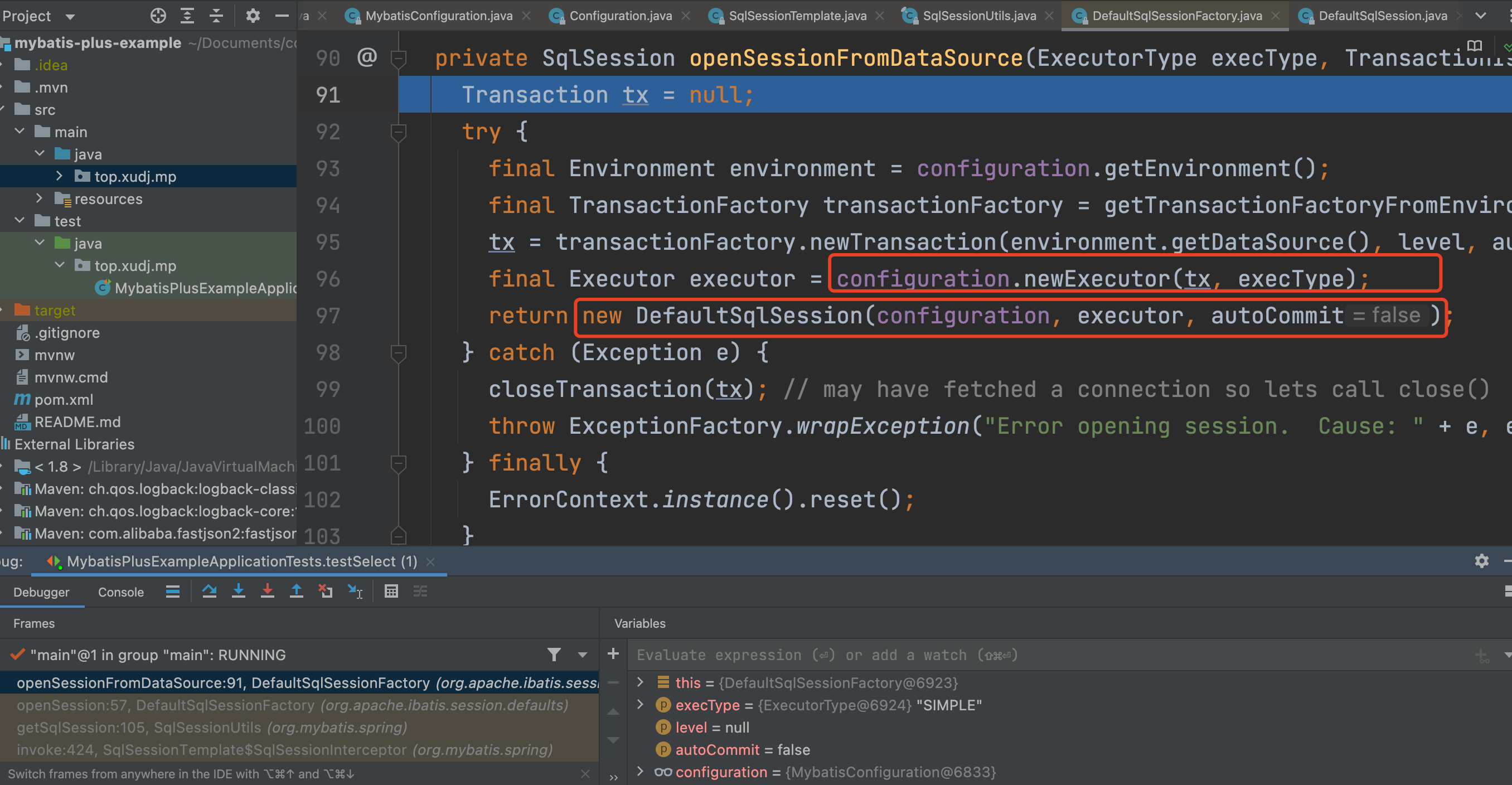
创建Executor时会通过动态代理类Plugin完成拦截器的扩展,后面可以另写文章解释。
Environment保存了数据库DataSource对象,用于创建事务
9、创建完sqlSession(DefaultSqlSession),反射执行对应方法 ,如下
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
最后的最后通过java.sql.PreparedStatement对象完成底层sql查询
总结
1、通过BaseMapper接口的方法查询,实际用的是代理类MybatisMapperProxy进行查询。
2、MybatisMapperMethod拷贝于Mybatis的MapperMethod,主要添加了分页查询的场景。
3、MybatisMapperMethod依靠于SqlSessionTemplate进行查询,SqlSessionTemplate依靠于DefaultSqlSession进行查询。
4、在创建DefaultSqlSession时,会创建事务、执行器等,最后会依赖于执行器Executor完成查询,在Executor查询前借助动态代理类Plugin加入了拦截器Interceptor的执行,核心类MybatisPlusInterceptor。