Spring事件
前言
Spring事件是为了在同一个ApplicationContext中多个Bean之间能够通信而设计的,给开发者提供了一种解耦的通信方式。也是观察者模式的一种实现。
我们先来了解下观察者模式。
观察者模式
定义对象之间的一种一对多依赖关系,使得当一个对象状态发生改变时,其相关依赖对象皆得到通知并被自动更新。
观察者模式的别名包括发布-订阅(Publish/Subscribe)模式、模型-视图(Model/View)模式、源-监听器(Source/Listener)模式或从属者(Dependents)模式。观察者模式是一种对象行为型模式。
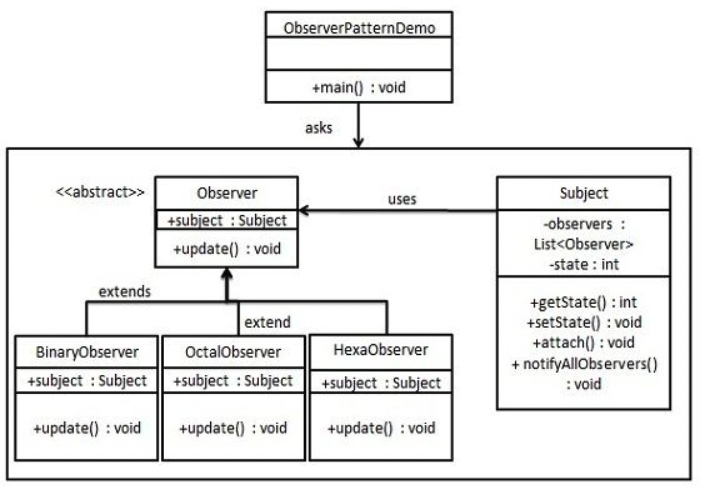
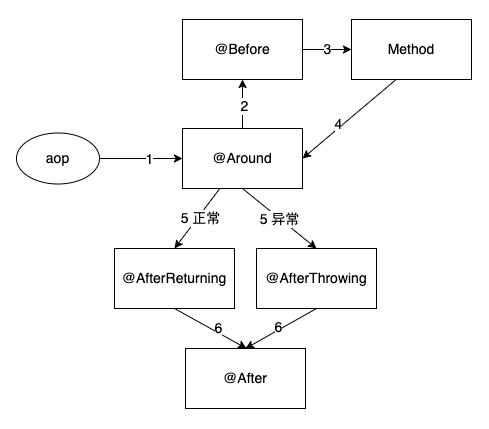
观察者模式实现样例类图。
JDK1.0已经设计了一套观察者模式的模型,核心API:Observable(被观察者)、Observer(观察者)。
// Observer(观察者)
public interface Observer {
void update(Observable o, Object arg);
}
// Observable(被观察者)
public class Observable {
private boolean changed = false;
private Vector<Observer> obs;
public Observable() {
obs = new Vector<>();
}
public synchronized void addObserver(Observer o) {
if (o == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!obs.contains(o)) {
obs.addElement(o);
}
}
public synchronized void deleteObserver(Observer o) {
obs.removeElement(o);
}
protected synchronized void setChanged() {
changed = true;
}
/**
* If this object has changed, as indicated by the
* <code>hasChanged</code> method, then notify all of its observers
* and then call the <code>clearChanged</code> method to indicate
* that this object has no longer changed.
* <p>
* Each observer has its <code>update</code> method called with two
* arguments: this observable object and the <code>arg</code> argument.
*/
public void notifyObservers(Object arg) {
Object[] arrLocal;
synchronized (this) {
if (!changed)
return;
arrLocal = obs.toArray();
clearChanged();
}
for (int i = arrLocal.length-1; i>=0; i--)
((Observer)arrLocal[i]).update(this, arg);
}
// ....
}
基于JDK的这种观察者模式已经在JDK9中被标记弃用,原因如下:
1、新加的观察者可能错过正在进行的通知,最新取消注册的观察者可能被错误的通知。
2、相互引用、耦合,如果在观察者中不慎调用了状态的更新,可能导致非预期的结果。
3、缺乏错误处理:update失败了,无法抛出受检异常,只能抛出运行时异常。
4、改变状态与通知观察者混着一起:每次需要通知被观察者时,必须要先更新change状态,使操作变得复杂;同时存在线程安全问题,如一个线程改状态,另一个线程通知。
5、缺乏灵活性:对Observable提供的对Observer api的操作比较有限。
再来看看java中的事件机制。
Java事件机制
在JDK1.1时候,事件处理模型采用了基于观察者模式的委派事件模型。
角色
Event Source:事件源,事件发生的地方/主体,也具有事件触发的能力。
Event Object:事件对象,传递信息的载体,一般作为参数存在于Listerner的回调方法之中。所有的事件对象都从Java中的EventObject派生而来。
EventListener:事件监听器,当事件源变化时,触发事件,回调事件监听器进行处理。所有事件监听器必须扩展EventListener接口。
简单示例
1、事件类,封装事件源和一些与事件相关的参数,继承EventObject类。
/**
* 事件类,封装事件源和一些与事件相关的参数
*/
public class DoorEvent extends EventObject {
/**
* Constructs a prototypical Event.
*
* @param source The object on which the Event initially occurred.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if source is null.
*/
public DoorEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
2、事件监听器,定义回调方法,事件源发生相应的事件时会回调该方法。继承EventListener接口。
/**
* 事件监听器
* 定义回调方法,事件源发生相应的事件时会回调该方法
*/
public interface DoorListener extends EventListener {
/**
* 处理事件
* @param doorEvent 事件
*/
void onDoorEvent(DoorEvent doorEvent);
}
/**
* 事件监听器的实现类
*/
public class BellRangDoorListener implements DoorListener {
@Override
public void onDoorEvent(DoorEvent doorEvent) {
System.out.println("门铃响了");
}
}
3、事件源,事件发生的地方,由于事件源的某项属性或状态发生了改变引发某个事件发生。
/**
* 门铃响事件源
* 事件发生的地方,由于事件源的某项属性或状态发生了改变引发某项事件发生
*/
public class DoorSourceObject {
private boolean state;
// 监听器
private Set<DoorListener> doorListenerSet = new HashSet<>();
// 给事件添加监听器
public void addDoorListener(DoorListener doorListener) {
this.doorListenerSet.add(doorListener);
}
/**
* 通知
*/
private void notifyListener() {
Iterator<DoorListener> iterable = this.doorListenerSet.iterator();
while (iterable.hasNext()) {
DoorListener doorListener = iterable.next();
doorListener.onDoorEvent(new DoorEvent(this));
}
}
/**
* 状态变化
* @param state
*/
public void setState(boolean state) {
this.state = state;
notifyListener();
}
}
4、测试类
public class Demo {
/**
* 模拟客户端
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoorSourceObject doorSourceDemo = new DoorSourceObject();
doorSourceDemo.addDoorListener(new BellRangDoorListener());
// 状态变化
doorSourceDemo.setState(true);
}
}
输出:
门铃响了
优缺点
相比观察者的 优点:
1、松耦合性:通过事件对象(EventObject)作为中介,将事件源(被观察者)和事件监听器(观察者)解耦
2、更丰富的事件类型:事件对象(EventObject)可以包括更丰富的信息,不仅可以携带触发事件的对象,还可以附带其它相关的数据完成特定的处理。
当前实现的 缺点:
1、不支持异步事件。
2、不支持异常处理:异常需要监听器自行处理,不然会影响其它监听器执行。
3、管理事件监听器的冗余与维护:事件源中关联着特定事件,且一些公共的添加和通知方法没有进行抽离复用。
Spring事件
Spring框架提供了一个强大且灵活的事件机制,能够轻松地实现事件的发布和订阅,使应用程序更加灵活、可扩展和可维护。
Spring事件是基于观察者模式的事件驱动编程机制。
概念
事件(ApplicationEvent):Spring事件的抽象基类,用于派生自定义事件,标识着某一类事件。
事件源(EventSource):事件发生的源头,事件初始化时传递给事件的对象。
事件监听器(ApplicationListener):订阅特定的事件,当事件产生时,监听该事件的监听器被触发通知回调。
事件发布器(ApplicationEventPublisher):定义了发布事件的方法,在实现类中,在适当时机发布特定事件。
事件广播器(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster):用于管理事件监听器和事件的广播,将事件传递给订阅该事件的监听器,作为事件发布器的代理。
核心API
参考《Spring事件核心API》一篇介绍,传送门->
简单示例
1、定义事件
/**
* 自定义spring事件
* @see ApplicationEvent
*/
public class MySpringEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
/**
* 创建一个事件
* @param message:消息
*/
public MySpringEvent(String message) {
super(message);
}
@Override
public String getSource() {
return (String) super.getSource();
}
public String getMessage() {
return getSource();
}
}
2、定义监听器
/**
* 自定义Spring 事件监听器
* @see ApplicationListener
* @see MySpringEvent
*/
public class MySpringEventListener implements ApplicationListener<MySpringEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MySpringEvent event) {
System.out.printf("[线程 :%s] MySpringEventListener - 监听到 Spring 事件:%s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), event);
}
}
3、通用测试
/**
* 自定义事件处理示例
* @see AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
* @see MySpringEventListener
*/
public class CustomSpringEventDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 将引导类 ApplicationListenerDemo 作为 Configuration Class
context.register(CustomSpringEventDemo.class);
// 1、添加自定义事件监听器
context.addApplicationListener(new MySpringEventListener());
context.addApplicationListener(new MyApplicationListener());
// 2、启动 应用上下文,会初始化 ApplicationEventMulticaster,发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
context.refresh();
// 3、发布事件
context.publishEvent(new MySpringEvent("hello kz"));
// 4、关闭上下文,会发布ContextClosedEvent事件
context.close();
}
static class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
println("MyApplicationListener - 监听到 Spring 事件:" + event);
}
}
@EventListener
@Order(2)
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
println("@EventListener(onApplicationEvent) - 接收到 Spring ContextRefreshedEvent");
}
private static void println(Object msg) {
System.out.printf("[线程 :%s] %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msg);
}
}
输出:
[线程 :main] @EventListener(onApplicationEvent) - 接收到 Spring ContextRefreshedEvent
[线程 :main] MyApplicationListener - 监听到 Spring 事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4361bd48, started on Thu Jul 06 18:00:00 CST 2023]
[线程 :main] MySpringEventListener - 监听到 Spring 事件:com.mainto.spring.event.spring.MySpringEvent[source=hello kz]
4、异步&异常处理测试
/**
* 异步事件处理器
* @see GenericApplicationContext
* @see SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
* @see org.springframework.util.ErrorHandler
*/
public class AsyncEventHandlerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
// 1、添加自定义事件监听器
context.addApplicationListener(new MySpringEventListener());
// 2、启动 应用上下文
// 会初始化 ApplicationEventMulticaster,发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
context.refresh();
// 获取ApplicationEventMulticaster
ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster = context.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (applicationEventMulticaster instanceof SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster) {
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster simpleApplicationEventMulticaster =
(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster) applicationEventMulticaster;
// 同步转异步
ExecutorService taskExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(new CustomizableThreadFactory("my-spring-event-thread-pool "));
simpleApplicationEventMulticaster.setTaskExecutor(taskExecutor);
// 添加异常处理
simpleApplicationEventMulticaster.setErrorHandler(e -> {
System.err.println("spring 事件异常,原因:" + e.getMessage());
});
}
// 故意抛出异常,监听器
context.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<MySpringEvent>) event -> {
throw new RuntimeException("监听器抛出异常");
});
// 3、发布事件
context.publishEvent(new MySpringEvent("hello kz"));
// 4、关闭上下文,会发布ContextClosedEvent事件
context.close();
}
}
输出:
[线程 :my-spring-event-thread-pool 1] MySpringEventListener - 监听到 Spring 事件:com.mainto.spring.event.spring.MySpringEvent[source=hello kz]
spring 事件异常,原因:监听器抛出异常
Spring内置事件
通过示例看看Spring中一些常见的事件有哪些,方便在业务需要的时候进行监听。
Spring 上下文相关
/**
* spring事件顺序示例
* @see AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
*/
public class SpringEventOrderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 添加自定义事件监听器
context.addApplicationListener(new ApplicationEventListener());
// 启动 Spring 应用上下文
context.refresh(); // ContextRefreshedEvent
// 启动 Spring 上下文
context.start(); // ContextStartedEvent
// 停止 Spring 上下文
context.stop(); // ContextStoppedEvent
// 关闭 Spring 应用上下文
context.close(); // ContextClosedEvent
}
static class ApplicationEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.println("事件:" + event);
}
}
}
输出:
事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4361bd48, started on Thu Jul 06 21:32:57 CST 2023]
事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextStartedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4361bd48, started on Thu Jul 06 21:32:57 CST 2023]
事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextStoppedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4361bd48, started on Thu Jul 06 21:32:57 CST 2023]
事件:org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent[source=org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4361bd48, started on Thu Jul 06 21:32:57 CST 2023]
Spring Boot相关
// 在spring启动项目的main函数中增加
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(Application.class);
springApplication.addListeners((ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>) event -> {
System.out.println(event);
});
springApplication.run(args);
输出:
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationContextInitializedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication@21fddaf3]
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationPreparedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication@21fddaf3]
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerInitializedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer@315893e7]
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationPreparedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication@21fddaf3]
org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@20a7d6db, started on Thu Jul 06 21:22:39 CST 2023]
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationPreparedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication@21fddaf3]
org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@20a7d6db, started on Thu Jul 06 21:22:39 CST 2023]
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication@21fddaf3]
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication@21fddaf3]
小结
通过执行顺序的测试,可以得到一个结论,当观察者观察某个事件时,发布该事件或该事件的子类事件,观察者均能收到通知。
总结
Spring事件机制是一种强大且灵活的事件驱动编程模式,能够实现松耦合的组件通信。通过使用Spring的核心API,我们可以轻松地定义自定义事件、订阅特定类型的事件(Spring内置事件),并在事件发生时执行相应的逻辑。Spring事件机制为应用程序提供了一种可扩展和可维护的方式来实现事件驱动编程。
希望大家能够深入了解相关概念、示例及核心API,并能于项目中灵活运用。